This site is intended for Indian residents.
Robotic-assisted technology is changing the way knee replacement surgery is planned and performed. It combines the expertise of your surgeon with advanced tools designed to enhance precision and control during surgery.
With robotic assistance, your surgeon can create a personalized surgical plan based on the unique shape and condition of your knee. During the procedure, the technology helps the surgeon follow this plan with a high degree of accuracy – supporting the careful placement of implants and helping protect surrounding soft tissues.
For patients, this means a procedure that’s tailored to their individual anatomy, performed with consistency and attention to detail – all guided by their surgeon’s skill and experience.
Experience severe knee pain or stiffness caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, or other forms of joint degeneration.
Find that non-surgical treatments such as medication, physiotherapy, injections, or bracing – no longer provide enough relief or allow them to move comfortably.
Have early to mid-stage osteoarthritis that affects only part of the knee joint, rather than all three compartments.
Total hip replacement
Robotic-assisted technology is changing the way hip replacement surgery is planned and performed. It combines your surgeon’s skill and expertise with advanced tools designed to enhance precision, accuracy, and consistency during surgery. Before the procedure, detailed images of your hip joint help create a personalized surgical plan based on your unique anatomy. During surgery, the robotic system assists the surgeon in following that plan with a high degree of accuracy – supporting the proper placement and alignment of the implant while helping to preserve healthy bone and surrounding tissue. For patients, this approach can provide a more tailored experience and added confidence in their procedure. Many people appreciate that robotic-assisted techniques are designed to support smooth joint movement and a more natural feel after recovery.
Experience severe hip pain or stiffness caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, avascular necrosis, or other degenerative joint diseases.
Have not found enough relief with non-surgical treatments such as medication, physiotherapy, lifestyle changes, or joint injections.
Robotic-assisted technology can help lead to better outcomes, like less pain1 and shorter recovery times1, compared to manual surgery.
In clinical studies, compared to manual surgeries, robotics:
Before surgery, a CT scan of your knee or hip is taken and used to develop a 3D virtual model of your unique joint. This helps the surgical team understand your unique anatomy.
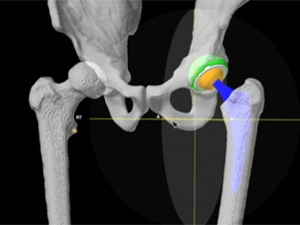
Next, the surgeon performs patient-specific surgical planning using the 3D model. They assess your bone structure, the severity of joint damage, overall alignment, and surrounding tissues. This allows them to determine the ideal implant size, placement, and alignment tailored to your anatomy.
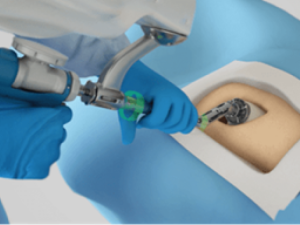
In the operating room, the surgeon uses a robotic-arm–assisted system to precisely remove arthritic bone and cartilage.
The technology creates virtual boundaries that provide feedback and help the surgeon stay within the pre-defined plan.
During the procedure, the system also provides real-time data on joint movement and soft-tissue tension, enabling the surgeon to make adjustments as needed for optimal accuracy.
References:
The information provided on this website is for general informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment options. Stryker does not dispense medical advice. This website may include contact details of hospitals, shared solely to help patients identify and contact healthcare facilities. Inclusion in this contact list does not imply endorsement, affiliation, or recommendation by Stryker India Pvt. Ltd. (“Stryker”). The information displayed is published with the consent of the respective institutions and is believed to be accurate at the time of posting. Stryker shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, or consequential damages arising out of or in connection with the use or misuse of the content on this website or the services of any listed providers. This website may contain links to external websites not operated or controlled by Stryker. We are not responsible for the content, accuracy, or privacy practices of such external sites. All content on this website, including text, graphics, logos, and other materials, is the property of Stryker or its licensors and is protected under applicable intellectual property laws. Unauthorized use is strictly prohibited. Stryker reserves the right to modify or update this disclaimer at any time without prior notice. Continued use of the website constitutes acceptance of any changes made.