This site is intended for Indian residents.

There’s no single path to managing knee pain – your treatment depends on your needs, lifestyle, and the condition of your joint. Most doctors will start with treatments that aim to reduce swelling, ease pain, and improve movement without surgery. But if those options don’t bring enough relief, your doctor may discuss surgical treatments to help you move more freely again.
Simple changes can sometimes make a big difference.
Your doctor may recommend:
These approaches can help you stay active and manage symptoms in the early stages of arthritis.

If non-surgical treatments aren’t enough to relieve your pain, your doctor may suggest knee replacement surgery.
Thanks to advances in medical technology, knee replacement today is more precise and personalized than ever before. Depending on how much of your knee joint is affected, your doctor may recommend either a partial knee replacement or a total knee replacement. Both procedures aim to relieve pain, restore movement, and help you get back to the activities you enjoy.
Total knee replacement
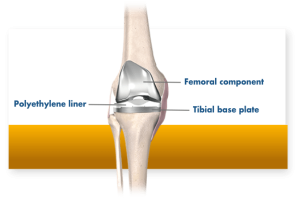
During a total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, your surgeon removes the worn or damaged parts of your knee joint and replaces them with specially designed metal and plastic components called implants.
These implants are made to mimic the natural movement of a healthy knee, helping you move with greater comfort and stability.
Partial knee replacement
If arthritis is detected early and the damage is limited to one area of your knee, your doctor may recommend a partial knee replacement. In this procedure, only the affected part of the knee is replaced, preserving as much of your natural bone and tissue as possible.
i
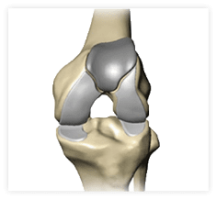
In a unicondylar knee replacement, only one area (or compartment) of the joint is replaced.
i
A patellofemoral knee replacement replaces the kneecap (or patella) and the grove at the lower end of the thighbone (or femur).
i
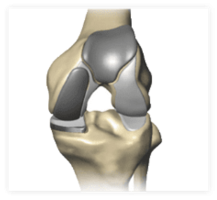
A bicompartmental knee replacement affects two compartments of the knee – the inside (medial) and knee cap.
Robotic-arm assisted knee replacement
Robotic-assisted technology is changing the way knee replacement surgery is planned and performed. It combines the expertise of your surgeon with advanced tools designed to enhance precision and control during surgery.
With robotic assistance, your surgeon can create a personalized surgical plan based on the unique shape and condition of your knee. For patients, this means a procedure that’s tailored to their individual anatomy, performed with consistency and attention to detail – all guided by their surgeon’s skill and experience.
The information provided on this website is for general informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment options. Stryker does not dispense medical advice. This website may include contact details of hospitals, shared solely to help patients identify and contact healthcare facilities. Inclusion in this contact list does not imply endorsement, affiliation, or recommendation by Stryker India Pvt. Ltd. (“Stryker”). The information displayed is published with the consent of the respective institutions and is believed to be accurate at the time of posting. Stryker shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, or consequential damages arising out of or in connection with the use or misuse of the content on this website or the services of any listed providers. This website may contain links to external websites not operated or controlled by Stryker. We are not responsible for the content, accuracy, or privacy practices of such external sites. All content on this website, including text, graphics, logos, and other materials, is the property of Stryker or its licensors and is protected under applicable intellectual property laws. Unauthorized use is strictly prohibited. Stryker reserves the right to modify or update this disclaimer at any time without prior notice. Continued use of the website constitutes acceptance of any changes made.